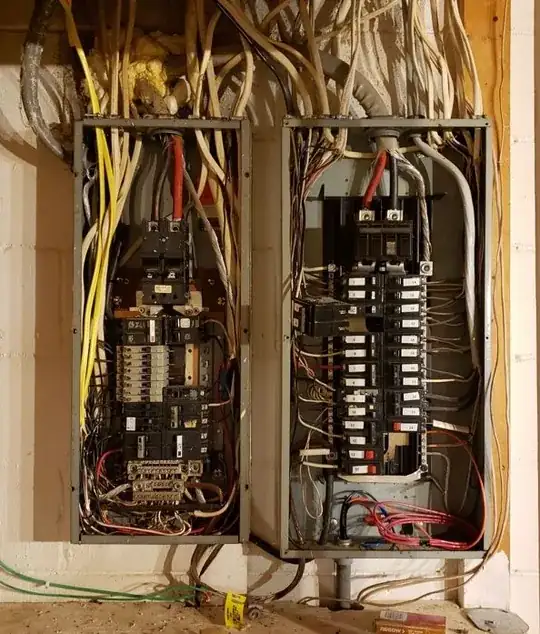
I believe I have two main panels that feed from one service line coming from the street. My assumption is they split the wire inside the wall with correctly sized wires to accomplish this (See older photo of opened panels).
I added a shop to my property and created a sub-panel on the right main. In my shop, I created a generator connection to feed power to my main(s) when the power goes out.
What I figured out last night when the power went out is that with the main breakers in the off position for both panels only the right main panel has power. I can not turn the mains to the on a position because this would cause power to go back up the service line potentially causing harm.
What I would like to know is, now in a power outage situation and with both main breakers off, how can I get power to the other (left) panel?
The left panel is the one I really need to be powered as it has our well pump and main light circuit on it.
- 7,241
- 3
- 28
- 42
- 175
- 2
- 4
- 14
4 Answers
You're already screamingly not safe because you don't have an interlock at all.
As discussed in multiple other answers, you cannot have a generator feeding a subpanel feeding the main, because that means no interlocks. The only thing a correctly wired generator input on a subpanel can feed is loads on that sub-panel.
So, you need a correctly interlocked generator input which is physically prevented from being on at the same time as the main on any panel you want to feed from a generator, and you either need an input for a portable generator that you move to that location, or you need an entirely separate set of wires from the generator location to that inlet/input.
- 235,314
- 11
- 293
- 637
Any safe suggestions?
"Checklist procedures" are NOT safe.
An axiom of electrical design is that we don't rely on "checklist procedures" to assure electrical safety. Your setup requires a fairly convoluted procedure to disconnect the panels from the grid and get generator power into (at least one of) them.
The US Marines have a saying. There's a myth that in a crisis, people will find some hidden clarity-of-mind and wisdom. Untrue: "People don't rise to a crisis - they fall back to the level of their training". And that's why the US Marines and friends train so darn hard. If you've followed the news in the last month, you see this (or its lack) on full display.
So NEC is very clear that you need to have mechanical interlocks to physically prevent dangerous configurations from being set.
If you think about it earnestly, they're right. You could mess up in the stress of it. What if you're not there and a family member asks a neighbor? They're not going to get it right. They're going to throw switches madly, trying everything. And they're going to stop at the first combination that seems to work.
By the way, power companies are draconian toward people caught back-feeding and can cause rather serious knock-on effects for those caught. Which smart meters make easier.
What these panels are
What you have here is 400A service, also called "Class 320" (the power company sees it as a 320A "continuous load"). 400A breakers are prohibitively expensive today, and were even moreso when this installation was done. So the bog-standard way of installing 400A service is to have a "Meter Pan" outside with and dual 250 kcmil lugs at the bottom. From those lugs, 250 kcmil (sometimes 4/0) wire is run to each of two main panels. Each main panel has a 200A breaker.
That's what you're looking at. There is no split "in the walls" (junctions are never buried, all boxes must remain accessible forever)... these service entrance cables go straight into the meter pan. Those cables are totally un-fused, and as much as 22,000 amps can flow if you drove a nail through one of them. As such, those cables are required to be as short as possible, and guarded as much as possible.
NEC 2020 now requires (indirectly) that the main breakers be part of the meter pan, so those lines now have circuit breaker protection.
Powering 2 panels from 1 generator: Move circuits.
Generally speaking, it's not possible, because of neutral problems. The only ways to do it are to have a transfer switch which switches neutral, or have a transformer that provides isolation.
Or the other way is to have a "master" transfer switch upstream of both panels. For instance coming direct off the meter to a 400A transfer switch, and then feed each panel from the transfer switch.
So, in 400A installations like yours, the path of least, um, resistance is almost always to simply designate ONE of the panels to be the "critical loads panel", and feed that panel only from the generator.
Now how do you move a circuit between panels? The obvious method is to re-route the Romex cable to enter the other panel. However, most smart installers mounting two panels will install a few conduit pipes between the two panels. Or some flex conduit could be installed between the bottoms of the panels. A circuit entering one panel can be "brought over to the other panel" by extending all wires except ground, including neutral, to the other panel via the conduit. Use wire nuts to extend those wires. THHN individual wires (sold by the foot at better stores) are usually used for this. Land the extended hot(s) on their new breaker and the extended neutral on the neutral bar. Rerouting the neutral seems silly but it's essential to avoid weird problems, NEC 300.3.
Physical interlock(s) at the panel
The Code legal way of doing what you're doing, trying to switch a whole panel, is a simple and inexpensive "sliding plate interlock". Most of the cost is in the engineering and certification, really. The sliding plate assures that your main breaker and your "backfeed generator breaker" cannot be on at the same time. Simple as that.
It requires the generator breaker, which is back-fed, to be placed at top left or top right, as the interlock physically requires.
On having the shop feeder double as a generator feeder
Yeah, nope, you can't do that. The reason is, it becomes impossible to make the interlocks work. (what? Very long Bowden cable? LOL)
The only correct advice is to run two separate feeders. Whenever people ask this before they do the installation, we tell them to do exactly that, and steer them into aluminum feeder, which is proven reliable for heavy feeders, and is a net savings actually.
Now let's talk about options from where you are.
If you ran conduit, we need to have a conversation about conduit size and how we can get 2 feeders in there (it's perfectly allowed).
Another option is to re-configure it so that the one feeder is the generator supply only and is wired to an interlocked breaker. This would mean you would need to run the generator to power anything in the shop.
Another option is what I call "permanent wiring, temporarily". You are free to wire something to be a particular way permanently... and then 3 days later wire it to be another way permanently. In the subpanel, you bring in the generator leads and cap them off. At the main panel, you permanently install interlock and generator breaker with nothing connected to it. When the power fails, you shut everything off, and "permanently" rewire the FORMER subpanel feeder to be ONLY a generator feeder, by moving wires at both ends. When power comes back on, you "permanently" disconnect it as a generator feed and restore it as a subpanel feed.
- 313,471
- 28
- 298
- 772
Assumption: your goal is to have a portable generator powering critical loads on both panels in the main house. You put the generator at the shop because it's is convenient to store and operate it there, prevents noise and CO from entering the house, and because you regard the shop feeder as a convenient way to carry power to the house.
Solution: The easiest way to achieve the above would be to let go of the idea of the generator operating at the shop. Put an inlet on the house wall feeding a load-side transfer switch near the two panels. This would achieve two things: 1) It allows you to feed circuits from both panels without moving circuits around from one panel to another. 2) It provides a failsafe interlock for both panels. With a load-side transfer switch you select some (6 to 12) circuits from either panel, route them via an external transfer switch where each one is switched from generator to utility individually. A small advantage is when city power comes back, all the unswitched circuits come back immediately.
A different solution, given the convenient location of the two panels next to each other, would be to move all critical loads to one panel, preferably the one with the shop feeder. Then you can install a main interlock on that panel and feed anything you want, except the non-critical things on the other panel. You still need to install an inlet and move the generator to the house
If you really want to keep the generator at the shop, you can't use the shop feeder wires. You need to install a new reverse feeder from the shop to the house with the interlock or load-side switch at the house ... it doesn't matter how far away the generator is.
- 49,543
- 6
- 70
- 201
Running two electrically isolated circuit breaker subpanels from one generator is absolutely do-able, provided your power plan calculation doesn't exceed the output from the generator. You'll need to have TWO ATS's feeding the two isolated circuit breaker panels. Power must also be isolated with separate feeds from the 400-amp SE panel to each of your two downstream ATS panels.
Generac makes this a very simple process - just run 2 transfer wires from one ATS to the secondary one. Search youtube for "Emergency Standby Generator Install, DIY Start to Finish. Generac 24kW Backup Generator." for more info. The top video is a good overview of the Generac two-panel setup.
My electrician just completed a Kohler install with two separate, electrically isolated, panels. Unfortunately, the Kohler install is not as simple as the Generac, because Kohler's electronics are significantly more complex than Generacs. My Kohler setup is as follows:
400-amp SE power from the street feeding a 200-amp Kohler ATS and Square-D 100-amp SE panel on the outside of the house
a Kohler RXT 200-amp SE ATS outside the house (the electronics of this ATS are used as the "Primary or Master ATS") - this 200amp ATS powers my 200amp circuit breaker panel in the basement
a Square-D 100-amp SE panel outside the house to isolate the Kohler RXT 100-amp combined ATS/CB panel in the basement
lastly, a Kohler RXT 100-amp combined ATS and 16-circuit breaker panel in the basement (this is configured as the "Secondary or slave ATS").
The kit that facilitates this is called the "Kohler KTSE-1 RXT Expander" made by PSP products. The setup instructions require a small modification of the Kohler RXT 200-amp ATS, and R&R of the Kohler RXT 100-amp "main board" and installing the PSP expander module (which was an additional $440) in its place.
Installation and configuration was very simple once the solution was identified, which was difficult at best because even the Kohler dealer (and supposed expert) wasn't familiar with this setup. Search youtube for "KTSE-1 Installation and Troubleshooting" for explanation and installation overview.
The bottom line is that two 200-amp, electrically isolated, circuit breaker panels CAN be configured with ONE generator (well, at least either the Kohler or Generac) provided electrical isolation (i.e. one of the 200-amp panels can NOT be a subpanel of the other), and load calculations don't exceed the generator capacity. In my case while I have two CB panels fed by 400-amp street service, the maximum load is only around 100-amps total.
I hope this helps. -Will