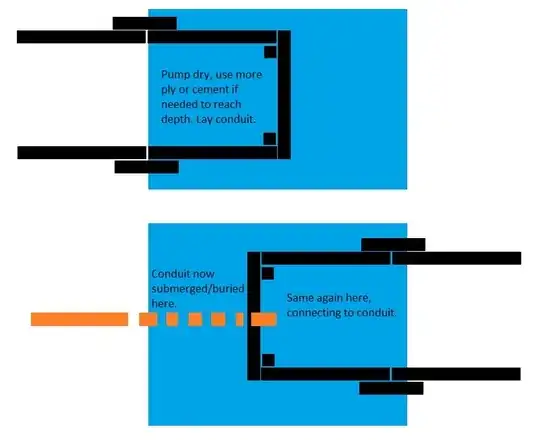
Short version: I need to run 4" PVC electrical conduit under a 4' wide creek where the water is usually 1-4" deep. Code in this area requires cable in conduit to be 18" deep. I do want to keep it that deep or, if I can manage it, maybe 24" deep so changes in the creekbed will not create any problems for it.
What I can do: I can dam up the creek just upstream and run the entire creek flow through a 4" PVC pipe. (I've done this before.) So that will stop the creek in that area. I also have a tractor with a backhoe, but I'm not sure I can get it down there without it sinking into soft dirt. I have a lateral bore system that requires water from a hose and an electrical drill for it to run a hole through dirt.
My concerns: I expect the groundwater level to be close to the water level in the creek, so when I start digging, I expect any holes to be filled with water. Also, a lot of the creek bed is sand, but I'm not sure how deep that goes. I know with sand, I have to start with a much wider opening than what I need at the bottom. I definitely can't use the lateral bore in a wet hole, since it uses an electrical drill.
Other thoughts: I don't know how fast a hole will refill with water after I pump it out. I've considered that it might be possible to dig the hole I need for the lateral bore system (which needs to be about 1-2' wide and about 5' long and a few inches deeper than the conduit) and use a garbage pump to keep water out of it while I'm using the bore. I also don't know if the ground 18-24" below the creek is firm enough for any hole I bore to remain until I can run conduit through it. The cable is outdoor rated and I know the rule that you assume any underground conduit has water in it, so I'm allowing for the idea that I may have to do some conduit work underwater and just accept water will be in it.
Code issues: Please, let's not get into issues with code unless there's a point that can make a difference. I have a few people answering technical questions for me, including one of the county inspectors. Anything I do on my own I run by him first and he tells me if it's in code or what I have to change. Often he has good ideas, but this is not something most people run into as an issue.
I'm looking for the easiest (and hope that's the best) way to get the conduit down in the ground, as required, in the wet environment of a creek and the groundwater around it. I'm not insisting on using the lateral bore. I don't mind digging. I just don't know how to deal with the wet environment and the likely issues of dirt and sand continually falling back into the hole.
(As a side note, this is tangentially related to this question.)
Addendum: I am not ignoring this or refusing to pick an answer. (Same with the question I link to above.) This is ongoing. I called in a contractor and he looked at the creek and looked at 220' of roadway I had built with heavily packed gravel on top and packed dirt below. This contractor and his men had, within the past few months, put in 10 drains in our driveway, which is part of this roadway, so he and his men personally know how packed it is. He looked over the creek and the roadway and said, "It's going to be easier to go through the roadway..."
But then he got here and his guys said, "Uh, dig up THAT roadway? We want to go through the creek."
When it's resolved, I'll add that info here. For picking the answer, since some include similar suggestions, I'll likely pick the one that considers the most details. (For instance, "Dig a trench through the creek," is not at all helpful. But providing ways to do that and deal with the groundwater and so on is useful and helpful.)
Addendum #2: The conduit is in place. I haven't pulled the wire yet, that'll be in the next few days. I was so exhausted from weeks of testing and digging holes that I hired a contractor I trust to help me with this. I had to do about 190' of trenches other than going under the creek, so I used a trencher and trenched right up to the creek on each side.
There were some good and creative answers provided. The problem with some is that they left out critical details or made assumptions. (For instance, one side of the creek bank was a 2-3' drop directly to the creek, which would make some ideas harder to do.) Ultimately, we had to block off water at the creek crossing (about 75' upstream) so the contractor and his men could build a cofferdam. They redirected water through a ditch they dug and later filled in. Once the cofferdam was in place, they removed the block at my creek crossing.
I want to point out that @Harper - Reinstate Ukraine included some key points nobody else did. For instance, he included issues with the electrical code. Ignoring those could have let to a failed inspection and a need to redo the whole project. Also, he included an important point that you always assume a conduit is full of water. (I knew this, but it bears clearly mentioning it!)
There were some answers talking about using concrete. While that might be under the creek, or part of the structure, the problem is that in many states the wetlands regulations do not allow any kind of structure in the wetlands without permitting. This can be a problem for local, state, and federal issues. (And you do NOT want to mess with the Army Corps of Engineers on something like this!)
As a side note, it took 4 men working about 9-10 hours on one day to handle controlling the water and getting the conduit in place. They came back another day to dismantle the cofferdam and do the remainder of the backfilling. Seeing how hard they worked convinced me that calling in help to do this was the right thing to do.