Insulation value of masonry walls vs wood-frame walls
You should be able to find guidance. For example Scottish Guidance, UK Guidance
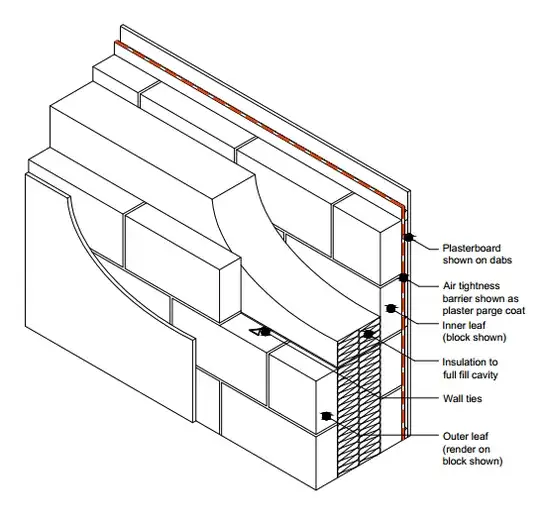
In the UK, I believe regulations specify maximum U-values
U-values are measured in watts per square metre per degree Kelvin (W/m²K).
So for example, if we consider a double glazed window with a U-value of 2.8, for every degree difference in temperature between the inside and outside of the window, 2.8 watts will be transmitted every square meter.
A range of possible U-values are indicated below for the purposes of comparison:
Solid brick wall 2.0
Cavity wall with no insulation 1.5
Insulated wall 0.3
Insulated roof 0.2
Single glazing 4.8
Double glazing 2.8
Low e double glazing 2
Triple glazing 1.5
Floor 0.2
Part L of the Building Regulations (Conservation of fuel and power) now prevents certain forms of construction by setting limiting standards (ie maximum U-values) for building elements.
More detailed advice on construction suggests various combinations of materials to meet U-value regulations.
So, if regulations in France were comparable to those in the UK you might need evidence that your constructed wall will have a U-value less than 0.28 W/m²K and that the overall building's U-values still meet regulations.
In France, I imagine your best bet is to find similar French specifications or EU specifications.
Some notes about U-values, R-Values etc
I have a small "Architects Pocket Book" ISBN 978-0-7506-8617-4 which contains all sorts of strange and wonderful information, including the following:
Thermal Conductivity (K Value)
The heat (W) transmitted through unit area (m²) of a material of unit thickness (m) for unit temperature difference (K) between inside and outside environments, expressed as W/mK
Thermal resistivity (R-value)
The reciprocal of thermal conductivity. i.e. mK/W. It measures how well a material resists the flow of heat by conduction.
Thermal resistance (R-value)
This measures how well a particular thickness of material resists the passage of heat by conduction, calculated from the R-value in units of m²K/W
Thermal transmittance (U-value)
The reciprocal of thermal resistance. i.e. W/m²K. This measures the amount of heat transmitted per unit area of a particular thickness per unit temperature difference between inside and outside environments.
U = 1 / (Rsi + Rso +Ra + R1 + R2 + R3 ... )
Where
- Rsi = thermal resistance of internal surface.
- Rso = thermal resistance of external surface.
- Ra = thermal resistance of air spaces within construction.
- R1 = thermal resistance of successive components.
Note that for wood frame construction I understand you have to average the U-values for the parts whose cross-section is all wood (where the wooden structural members are) and parts which contain voids or insulation-filled spaces. I assume this has to be an appropriately weighted average (by area of each type of cross-section).
