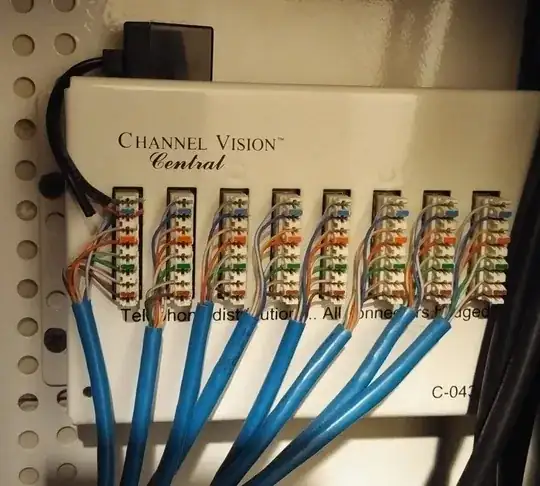
Yes, you can pull out your existing telco punchdown block and replace it with a suitable block for Ethernet networking.
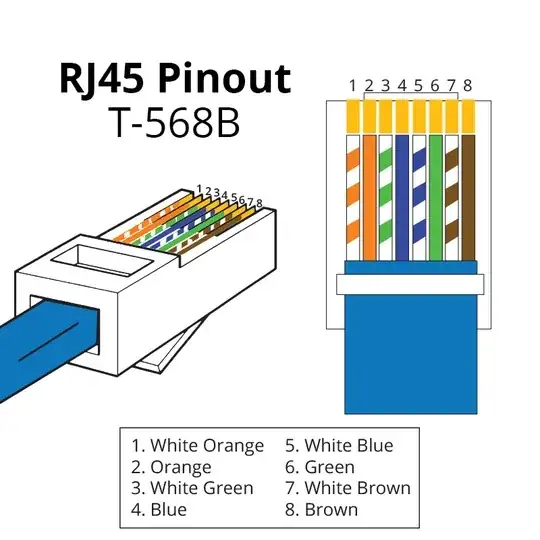
What you're really looking for is a Cat 5e (or better), T-568A or T-568B compatible punchdown block with RJ45 jacks. That's TIA/EIA-568 revision B, which is essentially identical to the older AT&T 258A (Systimax) standard, which was originally designed for telephone service. T-568A and T-568B are electrically compatible as long as the same standard is used on both ends of each segment. T-568A is still the official data networking standard, but a lot of vendors use T-568B. Whichever; just make sure the same standard is used on both ends of each individual length of cable.
So a typical structured cabling solution works for phones and data networking, although a residential solution may bridge tap all of the phone lines so all the extensions ring together, and that's completely incompatible with Ethernet networking. It's also easy to bridge tap multiple RJ45 ports together in the future if that becomes desirable.
Your new punchdown block
First confirm that those cables in the wall are Cat5e. If they're only Cat5, then you'll only be able to reliably use Fast Ethernet (100Mb/s), not Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mb/s).
You'll fasten your new punchdown block to the back of your media cabinet, then punch your incoming cables down to the new block. There's an example below (picture), but you can literally just walk into a big box store and grab one for $20 or so. Then you'll run short Ethernet patch cables between this punchdown block and your switch or router. T-568B is also compatible with telephones, so this upgrade won't prevent you or the next owner from using those existing wall jacks for telephone extensions later if you want to.

You'll want to confirm that your RJ45 wall jacks are wired up to the T-568B standard.
You'll fasten your switch(es) and/or router(s) to the back of your structured media enclosure as well, then you'll use short Ethernet patch cables to make connections from the switch/router ports to your wall jacks.
Someday you might want phones again
If you want to bridge some ports to turn on some telephone extensions in the future, you could easily do it with a little creative crimping of RJ-45 and/or RJ-11 plugs to connect all the right wires, which you would then plug into the RJ-45 jacks you want to connect phones to.
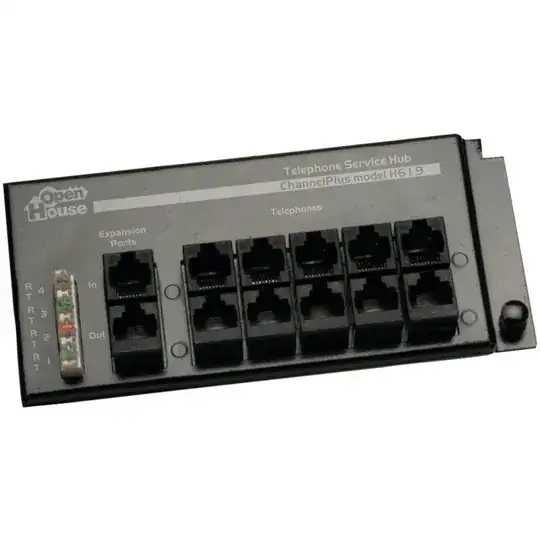
Or you could just buy a telephone interface hub similar to the one pictured below, which lets you adjust which jacks are bridged together using bridge clips. So you would snap on whatever bridge clips suit your purpose, then use regular telephone patch cables (2 or 4 wire) to connect the wall jacks to the telephone interface.
I guess I should clarify that you can plug RJ-11 (phone) plugs into RJ-45 jacks.